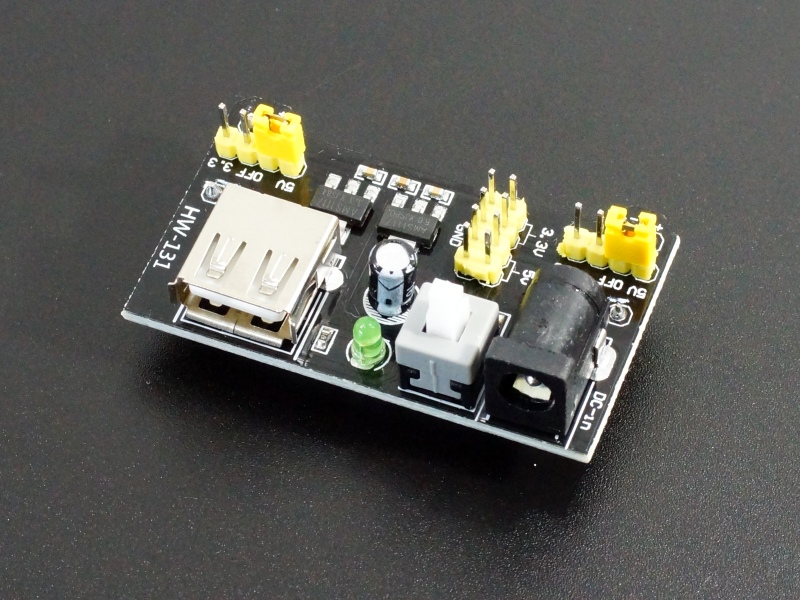
Breadboard Power Supply Module
$1.95
Provides 3.3 and 5V to solderless breadboard power rails.
59 in stock
Description
The Breadboard Power Supply Module plugs directly into a solderless breadboard and provides 3.3V and 5V power directly to the breadboard power rails.
PACKAGE INCLUDES:
- Breadboard Power Supply Module
KEY FEATURES OF BREADBOARD POWER SUPPLY MODULE:
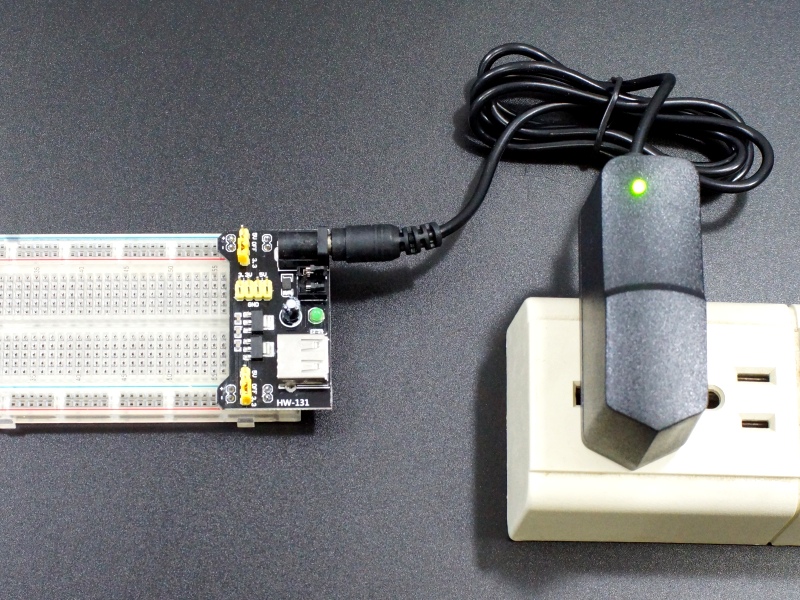
- Accepts 7-12V input via standard DC power jack
- Accepts 5V input via USB
- USB port can supply 5V power to MCU when using the DC power jack
- 3.3V or 5V can be individually selected for the left and right power rails.
- Can supply up to 400mA of current. See table down below for details.
- Power On/Off switch
This module provides an inexpensive and convenient way to convert a 7-12V wall bug into 5V and 3.3V to power a solderless breadboard setup. Being inexpensive, it does have some limitations but it works well as long as you stay within those limitations which are outline below. If you have a nice bench supply, this can be used to free-up your bench supply for other duties.
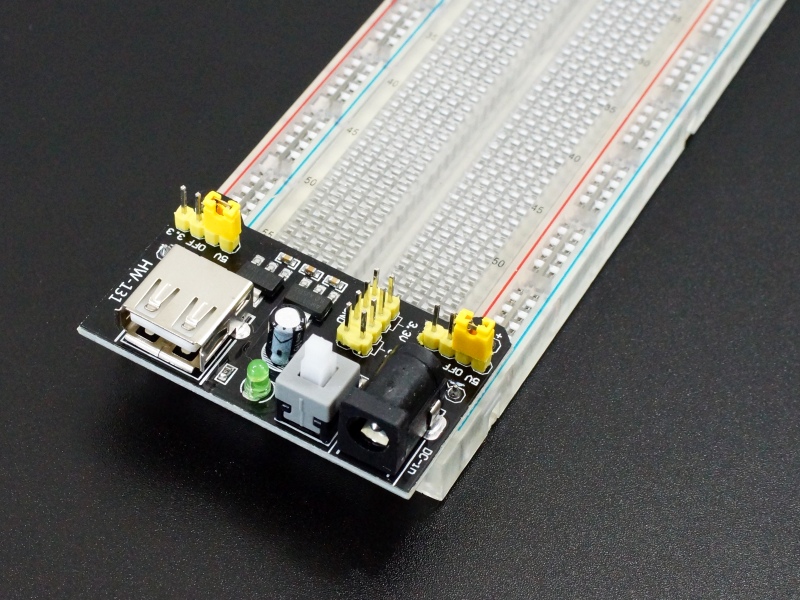
 Install Module On Breadboard
Install Module On Breadboard
The module plugs into one end of a standard breadboard.
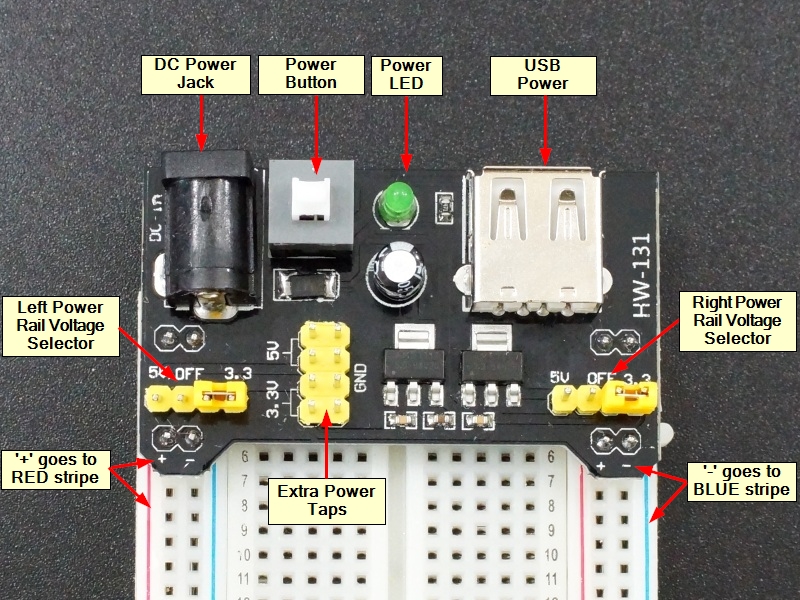
Be sure to insert the module into the correct end of the breadboard so that the +/- on the module line up with red/blue lines on the breadboard as shown. The plus sign should line up with the red stripe and the minus sign with the blue stripe.
The module has 2 sets of power pins on the bottom. If you install the module so that all of the pins are inserted, the module will be more secure but will block some of the breadboarding area. You can use the module with only 2 set of pins installed to avoid this, but the module will not be as stable.
Output Voltages
Jumpers on the board allow you to select either 5V or 3.3V for each of the 2 breadboard power rails.
Placing the jumpers in the center ‘OFF’ position removes the power from the that rail. Moving them to the left applies 5V and moving them to the right applies 3.3V. There is also a small header that provides another place to tap off 3.3V, 5V and GND if you need to.
Input Power
DC Power Jack:
Power can be input via a standard DC Power Jack. Input power should be kept between 7-12VDC when using the DC Power Jack. You will see specs on the internet that say you can go down to 6.5V on the input, but in our testing regulation started to drop out if the input drops below about 7V. The reason for that is there is a reverse protection diode on the input which is adding an additional voltage drop before the regulator.
The regulators can technically handle up to 15V on their inputs, but the output current will be more limited with higher input voltages as detailed in the table below and so 12V should be considered the upper limit. In general, running these off a 7-9V input will give you the best performance. We have a 7.5V 1A AC Adapter that works great with these modules or for mobile use our 9V battery to DC Plug adapter works well.
USB Power:
The module also has a USB (A-type) connector which you can use to power it off of if the other end is connected to a powered USB port such as on a computer or powered USB Hub. When this is used, the 5V from the USB is applied directly to the breadboard and also fed to the 3.3V regulator Note: Do not connect both a DC power plug and powered USB at the same time or damage may result.
This USB port can also be used as an output to power a device like an Arduino board that requires 5VDC using a USB cable when the module is powered off the DC Jack. When hooking up a device to power it off of the USB connector, make sure that device is not already powered by a different source or damage may result.
Power Control:
Power is controlled with a push on / push off button. The button does not have much tactile feel. so you will need to rely upon the power LED to tell you if power is on or off to the breadboard. The power button also controls power to or from the USB port.
OUR EVALUATION RESULTS:
For the price, these work really well for an inexpensive breadboard power setup.
Two AMS1117 regulators regulate the DC power input down to 5V and 3.3V. The output of the 5V regulator feeds the input of the 3.3V regulator. If you are using both voltages on your breadboard you need to add the current draw off the 3.3V regulator to the current draw off the 5V and stay within the maximum current draw as outlined in the table below.
As with any linear regulator, the power dissipation of the regulator is dependent on the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage. The larger the difference between the input and output voltage, the higher the power dissipation. For that reason, it is suggested to keep the DC input power in the range of 7-9VDC if you want to the maximum current available from the module.
The good news is that if you guess wrong on the current draw, the regulators have thermal protection built-in so if you draw too much power, they will safely shutdown before damage can occur. If that happens, you need to look for ways to reduce your power draw or perhaps use a lower voltage power source to power the module from to reduce the power dissipation. The regulators are also output short circuit protected, so accidentally shorting the outputs to ground won’t cause permanent damage. The only real way we have found to destroy one of these is to incorrectly hook up both a DC power plug and a powered USB source at the same time (so don’t do that…..).
The table below shows the maximum current draw that the module can handle with different input voltages. This includes the combined current from both the 5V and 3.3V rails.
Max Current Draw
| DC In | 5V + 3.3V current draw |
| 7V | 400mA |
| 8V | 400mA |
| 9V | 400mA |
| 10V | 300mA |
| 11V | 250mA |
| 12V | 200mA |
| 13-15V | 150mA (Not recommended) |
BEFORE THEY ARE SHIPPED, THESE MODULES ARE:
- Inspected
- Outputs are verified at 5V & 3.3V
- Packaged in a high quality resealable ESD bag for protection and easy storage.
Notes:
- Be sure to orient the module correctly on the breadboard so that power lines up with the red stripes. it is easy to mount it on the wrong end.
- Under high current loads, the components can get fairly warm to the touch.
- The header pins that plug into the breadboard may need a little tweaking to get them to line up.
Technical Specifications
| Maximum Ratings | ||
| VIN | Maximum Input Voltage | 15V (12V max recommended) |
| Minimum Input Voltage | 7V | |
| Operating Ratings | ||
| IO | Output Current (max continuous) | 400mA |
| Dimensions | L x W x H | 53 x 33 x 25mm |
| Datasheet | LD1117 Voltage Regulators |



 Install Module On Breadboard
Install Module On Breadboard


