7805 Voltage Regulator 5V / 1A
$0.69
Fixed linear regulator that can output 5V @ 1A
99 in stock
Description
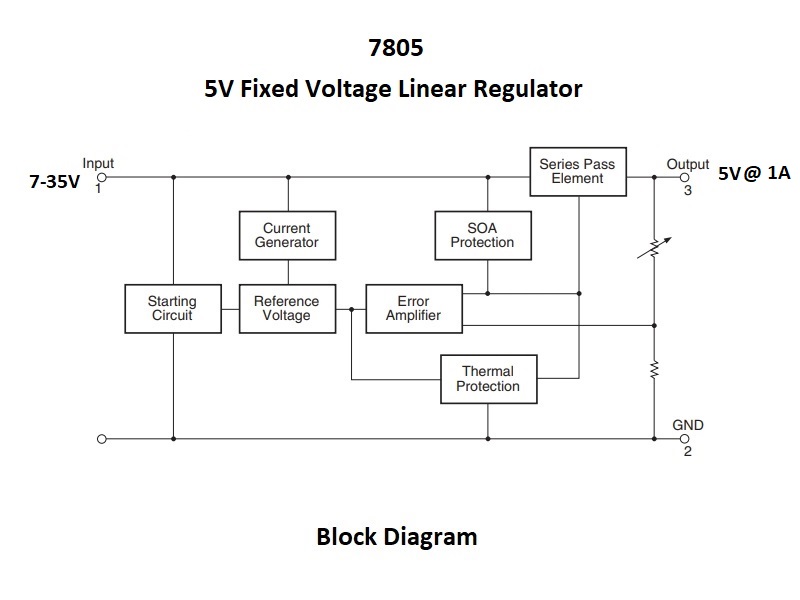
The 7805 is a fixed voltage linear regulator that outputs 5V at up to 1A current with an input voltage range of 7 – 35V.
PACKAGE INCLUDES:
- 7805 Voltage Regulator
KEY FEATURES OF 7805 VOLTAGE REGULATOR:
- Fixed voltage linear regulator
- 7-35V input voltage range
- 5V fixed output voltage
- 1A continuous current with 2.2A surge capability
- TO-220 package
The 78xx series of fixed-voltage linear regulators are some of the most popular linear regulators available and have been around for a very long time. They have built-in current limiting and over temperature protection and tend to be fairly robust devices. The prefix may vary depending on the mfr so you may see them listed as LM78xx, MC78xx, L78xx or just 78xx.
Basic Operation
The 7805 is perhaps the most commonly used linear regulator available. Input voltage can range from 7 – 35VDC and it outputs a fixed 5V at over 1A of current and up to 2.2A of surge current.
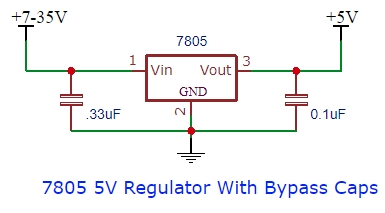
For basic operation, no external components are required. Just hook up the input voltage and ground and you have 5V available on the output.
If you are using it at a fair distance (> 10″) from the supply that is providing the input voltage, then a .33uF or larger input filter capacitor is recommended. The part ideally should be a low ESR part such as a Tantalum or Mylar capacitor, but small electrolytic caps generally work fine. An output capacitor of 0.1uF or larger can also be added to improve output transient response as shown below
Power Dissipation
Linear regulators have less ripple on their outputs compared to DC-DC converters that can be used for the same basic purpose, but the trade-off is that the linear regulators also tend to dissipate more heat in the process. The reason is that the linear regulator uses a series pass transistor on its output to drop the excess voltage.
The power dissipation of a linear regulator is dependent on the difference between the input voltage (Vin) and the output voltage (Vout) along with the amount of current that is being drawn from the regulator. The larger the voltage difference is between Vin and Vout, the higher the power dissipation will be which limits how much current can be drawn from the device.
The power dissipation of the 7805 device is easily calculated as Power Dissipation = (Vin – Vout) * Iout.
If the 7805 input is 9V and it is providing 1A of current, then Power Dissipation = (9V – 5V) * 1A = 4W. The 7805 TO-220 package will need to dissipate 4W of power. Under typical conditions, the device can dissipate about 1 – 1.25W before a heat sink becomes necessary, so in our example here, the device would need a heat sink. Maximum output current without a heat sink in this case would be limited to about 250 – 300mA and the device will be running in the range of 85-95°C.
If you instead ran the 7805 off a 7V input, Power Dissipation = (7V – 5) * 1A = 2W. Still pretty warm, but much more manageable than 4W. With no heatsink you could draw 500-700mA.
As a general rule, you always want to use as low of an input voltage as possible to minimize power loss though the device and maximize the output current available.
Notes:
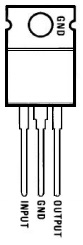
- The tab of the 7805 is common with the Ground pin.
- Under high current loads or with large input to output voltage differentials, the device can get very hot, so use care when handling.
Technical Specifications
| Maximum Ratings | ||
| VIN | Maximum Input Voltage | 35V |
| IO | Maximum Output Current | 1A (Typical) |
| IMAX | Peak Surge Current (typ) | 2.2A |
| Operating Ratings | ||
| VO | Output Voltage | 5.0V +/- 2% |
| VI – VO | Drop-out Voltage | 2.0V |
| Package | TO-220 | |
| Package Type | Plastic Tab, 3-lead, through hole | |
| Manufacturer | ON Semiconductor | |
| Datasheet | 7805 |