NE555 Timer Module
$1.49
Adjustable frequency and duty cycle of the square-wave output.
26 in stock
Description
The NE555 Timer Module incorporates the NE555 timer IC on a small board with the ability to adjust frequency and duty cycle of the output.
PACKAGE INCLUDES:
- NE555 Timer Module
KEY FEATURES OF NE555 TIMER MODULE:
- Operates NE555 in astable mode of operation
- Up to 500 kHz operation
- Frequency range jumper and adjustment pot for finer control
- Duty cycle adjustment pot
- 4.5 to 16V operation
The NE555 timer is one of the oldest chips around, but it is still useful for creating rectangular waveforms such as for lower speed clocking of circuits or for creating a timing pulse. If you check out the datasheet for the chip itself, it shows just how versatile the part is.
The bare NE555 chip which we also sell is fairly easy to use and only requires a couple of resistors and capacitors. The chip uses the RC time constants of the selected resistors and capacitors to set the output frequency and duty cycle. Once the novelty of wiring one of these up from scratch wears off, this little module includes all the parts required to implement the basic timing circuit (a-stable mode of operation) so that it can be easily included in a project or to use as a low cost frequency generator.
Setting Frequency
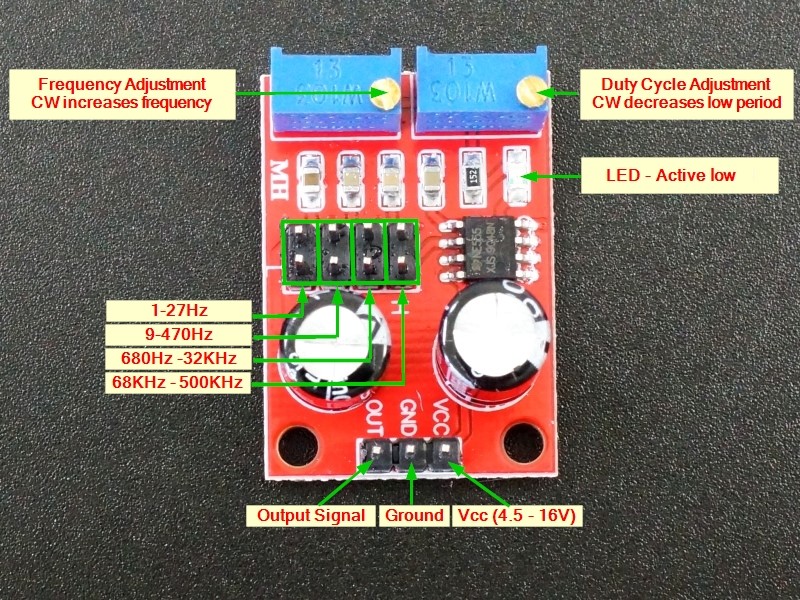
There is an 8-pin header that provides a jumper setting to select different frequency ranges.
The jumper puts different value capacitors in the circuit to change the time constant. The low end goes down to about 1Hz. The high end goes up to about 500kHz before the chip becomes unstable. The NE555 chip itself is actually guaranteed to 100kHz. As you push the frequency above that, the output becomes a little less rectangular until the chip eventually becomes unstable.
The multi-turn potentiometer near the frequency range jumper provides for fine control over the frequency once the basic range is set. Turning the pot CW increases the frequency, while turning it CCW decreases it.
The board includes an LED which is lit when the output is low and off when it is high. When the frequency is higher than about 30Hz, the LED will appear to always be lit since the blinking will be too fast to see.
The table below shows the range we measured on a sample basis. This will vary a bit between modules depending on the tolerances of the components used.
Frequency Select Jumper Ranges
| Jumper Position | Low Freq | High Freq |
| 1-L | 1Hz | 27Hz |
| 2 | 9Hz | 470Hz |
| 3 | 680Hz | 32kHz |
| 4 – H | 68kHz | 500kHz |
Setting Duty Cycle
The other potentiometer near the LED is a Duty Cycle adjustment that allows for changing the duty cycle of the output. The duty cycle refers to how long the output is driven high vs driven low. Turning the pot CW reduces the amount of time the output is low while increasing the amount of time that the output is high (increases duty cycle). This adjustment also has some affect on the frequency of the output.
The duty cycle is most stable at 50% or higher (high period is 50% or longer), especially at low frequencies. If the duty cycle is set too low, the output will go to a steady low. At higher frequencies, the duty cycle can be set to less than 50%, but the control is very touchy at duty cycles under 50%. See our eval results for more info.
Module Connections
There is a 3-pin male header on the module for making connections.
1 x 3 Header
- OUT = Signal Output
- GND = Ground
- VCC = 4.5 to 16V (5V typical for 5V logic compatibility)
The board has 2 holes which can be used for mounting it permanently if desired using two small screws.
OUR EVALUATION RESULTS:
This is a fairly handy little module and frankly cheaper than buying the components individually to build the same circuit. It’s not a replacement for a signal generator by any means, but it can be handy for generating basic timing signals or doing basic experiments requiring a square wave. The circuit is setup for A-stable mode of operation as per the datasheet which is linked below.
To understand what the output is doing requires an O’scope or at least a DVM or other tool with a frequency counter unless it is operating at very low frequencies under about 30 Hz in which case you can observe the operation by watching the LED. From our testing there can be gaps in the frequency range from one jumper position to another. This may or may not be an issue for your application.
The duty cycle adjustment is limited to a range of about 2:1, so 2 periods high to 1 period low or vice versa. If the duty cycle adjustment is run fully CW, the duty cycle will stretch out very quickly near the end of the pot travel and go constantly low when adjusted to the full limit of the pot.
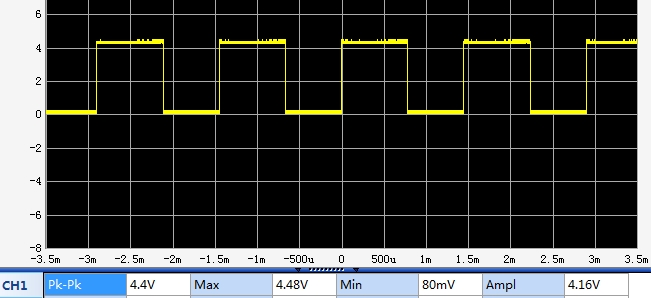
The scope capture below shows a typical waveform output from the module with it running on 5V power. Frequency is adjusted to about 680Hz. Logic low is 80mV, logic high is about 4.2V which are fine for TTL logic levels.
BEFORE THEY ARE SHIPPED, THESE MODULES ARE:
- Sample inspected and tested per incoming shipment
Notes:
- None
Technical Specifications
| Maximum Ratings | ||
| Vcc | Range | 4.5 to 16V |
| IO | Maximum Output Current | 200mA |
| Operating Ratings | ||
| Frequency | Per Spec | 1mHz – 100KHz |
| As Tested | 1 – 500KHz | |
| ILoad | 15mA @ 5V | |
| Dimensions | L x W x H | 31 x 23 x 18mm |
| Country of Origin | China | |
| Datasheet | NE555 |