ESP8266 D1 R2 WiFi Processor with Uno Footprint
$7.95
80MHz 32-bit WiFi enabled processor that uses the Arduino UNO footprint.
5 in stock
Description
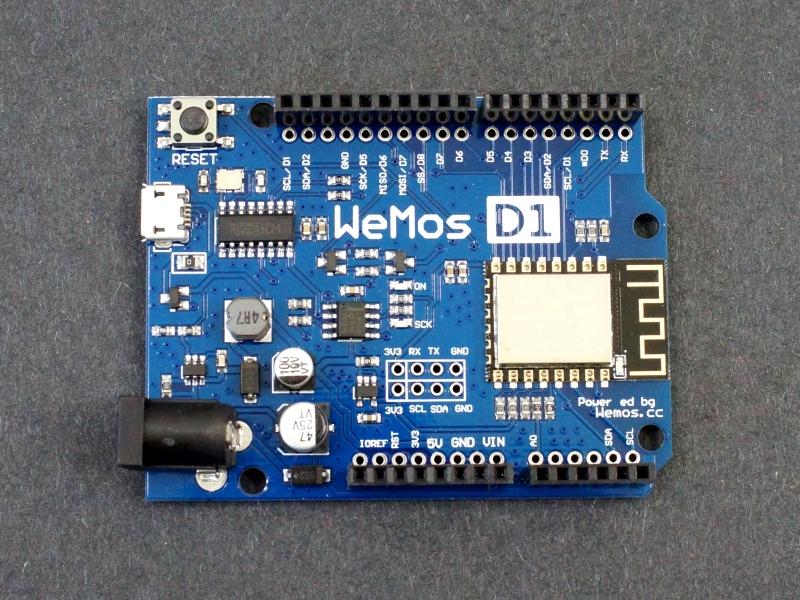
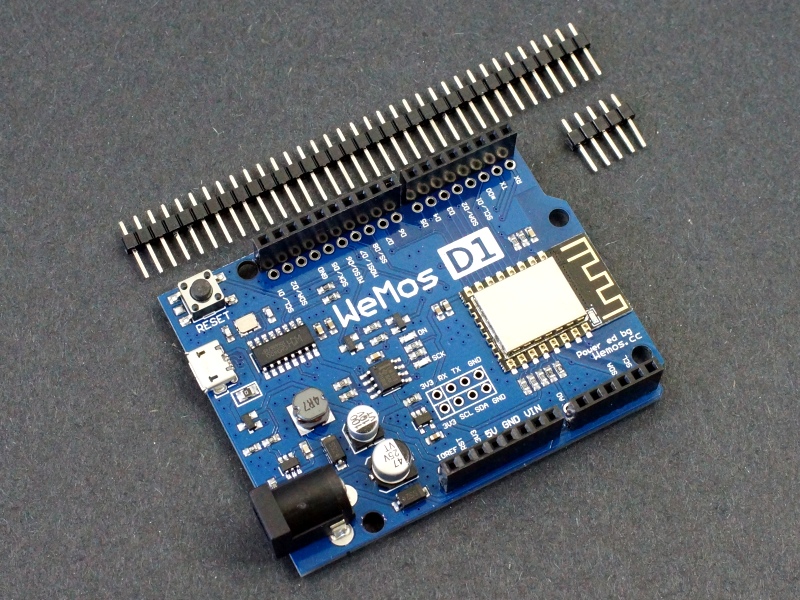
The ESP8266 D1 R2 WiFi board utilizes the ESP8266 WiFi enabled processor, and puts it onto an Arduino Uno board footprint. It provides a way to work with the ESP8266 in a familiar setup and does not require a breadboard in order to make interconnections since it has the typical on-board female headers. It will also work with some Uno shields that have compatible I/O pin-outs.
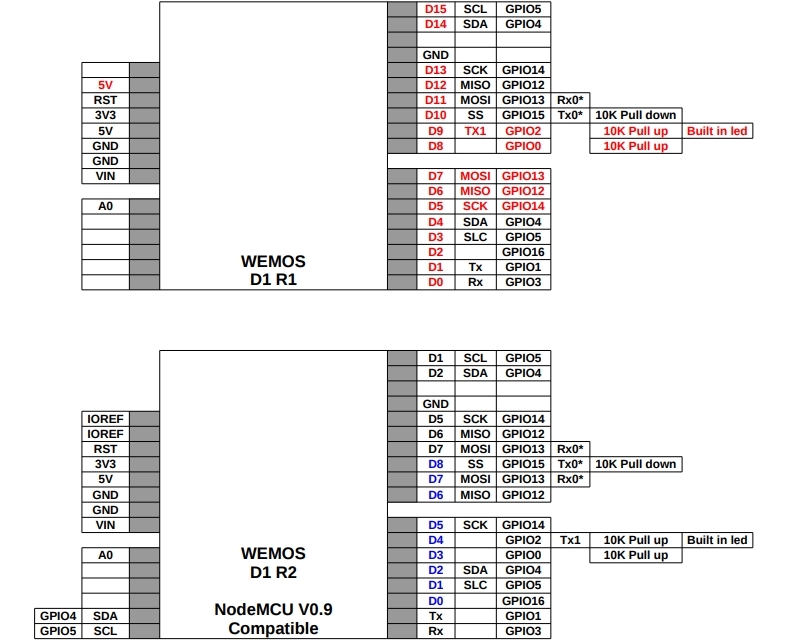
This board was originally produced by WeMos. This board is the 2nd generation R2 compatible version. There is also an earlier R1 version which uses a different pin-out on some of the I/O. The pinout on the R2 version was made to be more compatible with the NodeMCU pinout. If working with examples, you may need to reassign some pins depending on which version you are working with. One of the images shows the difference in the pin mappings between the two versions.
PACKAGE INCLUDES:
- ESP8266 D1 R2 WiFi with Uno Footprint
- Male header strip
Key Features of ESP8266 D1 R2:
- Microcontroller: ESP-8266 32-bit
- Clock Speed: 80MHz and up to 160MHz
- USB Converter: CH340G
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Flash Memory: 4MB
- Digital I/O: 11
- Analog Inputs: 1
- Communications: I2C, Serial, SPI
- WiFi: Built-in
Besides adding WiFi capability, the main claim to fame for the ESP8266 processor over the AVR processor of the standard Arduino is that it has a larger 4MB of Flash memory and runs at clock speeds of 80MHz and can sometimes optionally be overclocked to 160MHz and has a very fast processing speed.
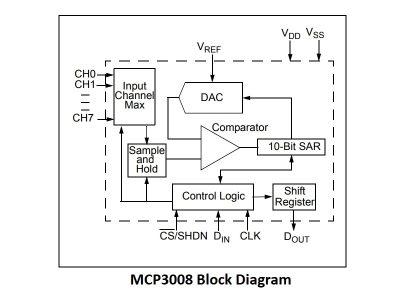
The Digital I/O except for D0 all support PWM and interrupts. In addition they can be configured to have pull-up or pull-down resistors On the down-side, it has only 1 analog input which is probably the most significant limitation. That can always be overcome by using an external Analog Mux module like our 16-channel 74HC4067, ADS1115 4-Channel 16-bit ADC or the MCP3008-I/P 8 channel A/D converter IC below if more analog I/O is desired.
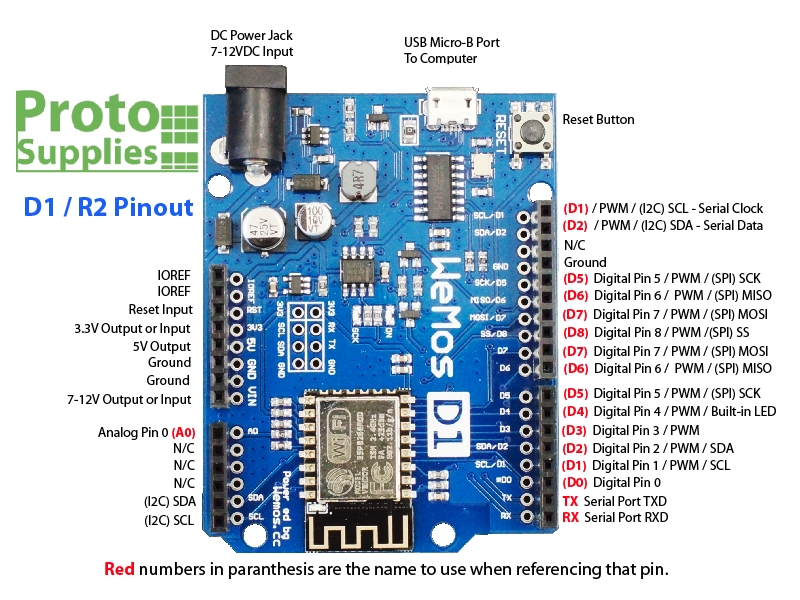
Note that when programming the board, you need to refer to the I/O using both the letter and number. With Arduino, output D3 would be referred to simply as ‘3’, but with the D1 board, you need to refer to the pin as ‘D3’.
Some of the pins are duplicated on the board such as D1, D2, D5, D6 and D7. The pins with the same names are physically connected together on the board. In addition, the I2C SDA/SCL expansion pins on the bottom left are also connected to D2 and D1. This gives a total of 9 digital pins (D0 – D8) plus RX/TX.
The board can be powered via the USB port or using an external 7-12V power supply via the DC Power Jack.
The board operates at 3.3V, so keep that in mind when working with I/O. Per spec, the digital I/O is limited to 3.3V, but the ESP-8266 mfr has made statements that the digital pins are in fact 5V tolerant and there are many installations using the module directly connected to the logic lines of 5V peripherals.
A nice feature on this version of the board is that besides the standard female headers for bringing out I/O, each female header also has a row of holes next to it to which can be soldered male headers, a second row of female headers or even wires. These can be soldered to either the top or bottom side of the board. The board comes with a strip of male headers which are normally soldered to the top side of the board. If the male headers are soldered to the bottom of the board, the board can’t be mounted directly into a breadboard since the separate sections of headers on one side are not spaced apart on 0.1″ centers and the holes are offset somewhat side-to-side.
It can be programmed using the Arduino IDE via the USB port as shown below.
Our Evaluation Results:
WeMos no longer makes these boards, so these are clone assemblies with good build quality
There are many instructions for installing and using ESP8266 based boards with the Arduino IDE, but here is a short-hand version.
- Open Preferences window and enter the following into the ‘Additional Board Manager URLs’ field: “http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json”.
- Under Boards Manager, install ESP8266 boards.
- Under Tools/Boards select “LOLIN WEMOS D1 R2 & Mini”.
- Select the port that the board is attached to
- Set comm rate to 115200 if using Serial Monitor Window
Below is one of the sample programs ‘Samples/ESP8266/Blink’ that are available once you install the ESP8266 files. It just blinks the blue LED on the ESP8266 module but is a good way to ensure your basic programming setup is working and the board is at least partially functional.
/* ESP8266 Blink by Simon Peter Blink the blue LED on the module This example code is in the public domain Note that this sketch uses LED_BUILTIN to find the pin with the internal LED */ void setup() { pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); // Initialize the LED_BUILTIN pin as an output } // the loop function runs over and over again forever void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // Turn the LED on (Note that LOW is the voltage level // but actually the LED is on; this is because // it is active low on the module) delay(1000); // Wait for a second digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED off by making the voltage HIGH delay(2000); // Wait for two seconds (to demonstrate the active low LED) }
Before they are shipped, these modules are:
- Inspected
- Powered up and the above example program ‘Blink’ is downloaded to verify basic operation.
- Repackaged in high quality resealable ESD bag for safe storage.
Notes:
- None
Technical Specifications
| Microcontroller | ESP8266 Tensilica 32-bit | |
| Serial to USB Converter | CH340G | |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V | |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V | |
| Digital I/O Pins | 11 | |
| PWM I/O Pins (Shared with Digital I/O) | 10 | |
| Analog Input Pins | 1 (10-bit) | |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 12mA (Max) | |
| Hardware Serial Ports | 1 | |
| Flash Memory | 4 MBytes | |
| Instruction RAM | 64 KBytes | |
| Data RAM | 96 KBytes | |
| Clock Speed | 80MHz | |
| Network | IEEE 802.11 b/g/n WiF | |
| Built-in LED | Attached to digital pin 13 | |
| USB Connector Style | Micro-B Female | |
| Board Dimensions (PCB) | 69 x 53mm (2.7 x 2.1″) | |
| Country of Origin | China | |
| Datasheet | ESP8266EX |