24LC256 I2C 256K-Bit EEPROM
$1.49
32K-byte EEPROM is used to provide non-volatile memory storage
7 in stock
Description
The 24LC256 32K x 8 (256K-bit) EEPROM is used to provide non-volatile memory storage with easy to access I2C interface.
PACKAGE INCLUDES:
- 24LC256 I/P DIP IC
KEY FEATURES OF 24LC256 256K-BIT EEPROM:
- 256K-bit memory organized as 32K x 8 bytes
- I2C Interface
- 3.3V and 5V compatible
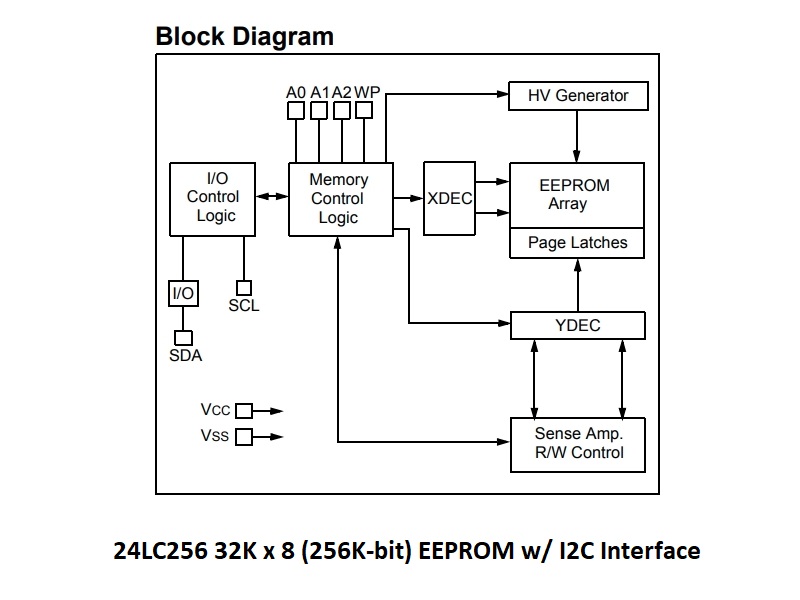
 The 24LC256 provides 256K bits of serial Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) organized as 32K words x 8 bits each.
The 24LC256 provides 256K bits of serial Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) organized as 32K words x 8 bits each.
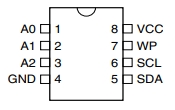
The device communicates via the I2C two-wire serial interface. The base I2C address is 0x50. Three address bits (A2, A1, A0) allow up to 8 devices to be used in the same system. To use a single chip at address 0x50, you can just ground all 3 address bits.
The Write Protect (PW) pin is grounded to allow normal read/write operations. If it is pulled high, the device is write protected and becomes a read only device.
These memories are sometimes used to store configuration information or data acquisition results.
OUR EVALUATION RESULTS:
These devices can be useful for adding non-volatile memory storage external to the MCU and are fairly easy to use.
The test program here uses raw I2C commands from the Wire.h library to exercise the device. It first writes the address of the memory locations to each of the first 256 memory addresses. So 0 is written to address 0 up to 255 being written to address 255. It then reads each of the locations to verify that the memory address and data match to ensure the write / read operation was successful. It then erases the device by writing 0’s to all those locations and then verifies that all locations contain 0.
To hook up the device:
- Connect 3.3V or 5V to Vcc pin to match MCU and ground to ground pin
- Connect I2C by connecting SCL to SCL pin and SDA to SDA pin
- Ground the WP
- Ground A0, A1 and A2 address pins
External EEPROM Test Program
/* Basic external EEPROM Test Program Write data 0-255 to addresses 0-255 Read data back out and print to serial monitor window Erase all data Verify data is erased. Print any not erased to serial monitor window */ #include <Wire.h> // for I2C #define I2C_Addr 0x50 // device address byte data = 0; // data to store in or read from the EEPROM bool data_error = false; //=============================================================================== // Initialization - Do everything here since running just once //=============================================================================== void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize the serial port Wire.begin(); // wake up the I2C // Write data to entire device Serial.println("Writing data..."); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) writeData(i, i); Serial.println("Writing Complete"); delay(1000); // Read data back out and print to Serial Monitor Serial.println("Reading data..."); delay(1000); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { Serial.print(i); Serial.print(" : "); data = readData(i); Serial.println(data, DEC); if (data != i) data_error = true; // Data should match address } if (data_error) { Serial.println("Error in data Write/Read operation, check log above"); data_error = false; } else Serial.println("Write/Read Completed Successfully"); delay(1000); // Erase the entire EEPROM Serial.println("Erasing all data..."); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { writeData(i, 0); // Write zeros to all memory locations } Serial.println("Erasing complete"); delay(1000); //Verify the erase operation Serial.println("Verifing data was erased..."); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { data = readData(i); if (data != 0) { Serial.print(i); // Print all non-zero memory addresses Serial.print(" : "); Serial.println(data, DEC); data_error = true; } } if (data_error) Serial.println("Error(s) in erasing found"); else Serial.println("EEPROM Erase Verified - Test Complete"); data_error = false; } //=============================================================================== // Sub writeData - Writes a byte of data to memory address //=============================================================================== void writeData(unsigned int addr, byte data) { Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_Addr); // set the pointer position //Wire.write((int)(addr >> 8)); Wire.write((int)(addr & 0xFF)); Wire.write(data); Wire.endTransmission(); delay(10); } //=============================================================================== // Sub readData - Reads a byte of data from memory address //=============================================================================== byte readData(unsigned int addr) { byte result; Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_Addr); // set the pointer position //Wire.write((int)(addr >> 8)); Wire.write((int)(addr & 0xFF)); Wire.endTransmission(1); Wire.requestFrom(I2C_Addr, 1); // get the byte of data result = Wire.read(); return result; } //=============================================================================== // Main - Nothing to see here.... //=============================================================================== void loop() { }
Notes:
- None
Technical Specifications
| Operational Ratings | ||
| Vcc | 2.5 – 5.5V | |
| Write/Erase Cycles | Min 1.000,000 | |
| Data Retention | > 200 years | |
| Package Type | Plastic body, DIP-8 | |
| Mfr | Microchip | |
| Datasheet | 24LC256 |